The share of people born in a state and who stay there can provide an important measure of its attractiveness to workers. The stickiness of native residents is also key to maintaining a stable (or growing) population and workforce, which is vital to economic growth.
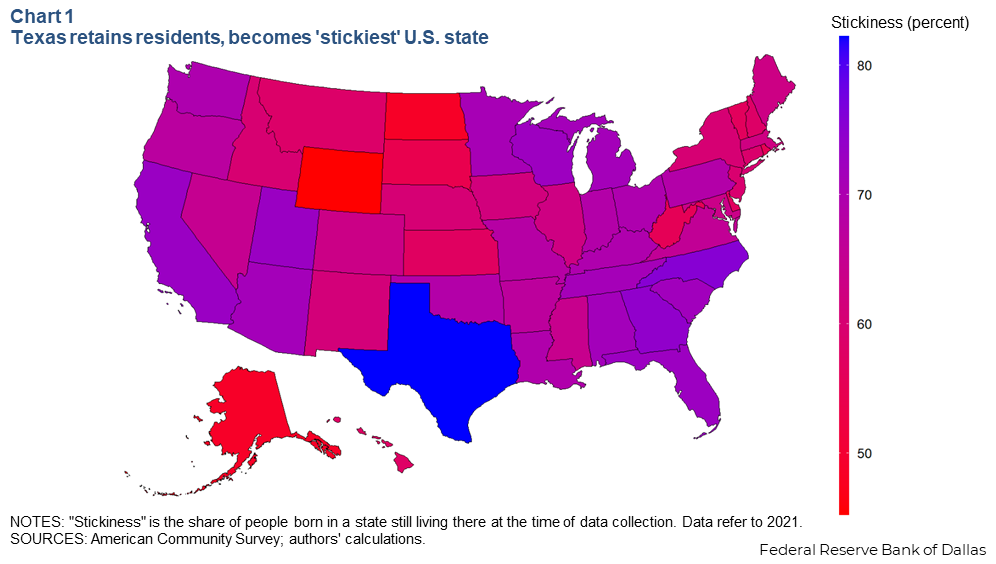
To figure out which states are best at retaining their native residents, we calculated the stickiness of each state. Using American Community Survey (ACS) data, we estimated the share of people born in each state who still lived in that state as of the 2021 survey (Chart 1).
Downloadable chart | Chart data
Texas is the stickiest state in the country by far, with approximately 82 percent of native Texans still living here in 2021. Other sticky states include North Carolina (75.5 percent), Georgia (74.2 percent), California (73.0 percent) and Utah (72.9 percent).
At the other end of the spectrum, Wyoming is the least-sticky state, with only 45.2 percent of natives remaining there. North Dakota and Alaska were the only other states with less than half their native population staying there (48.6 percent and 48.7 percent, respectively). Rhode Island (55.2 percent) and South Dakota (54.2 percent) round out the bottom five.
Notably, the least-sticky states tend to see high levels of outmigration of everyone—not just their native residents (Chart 2).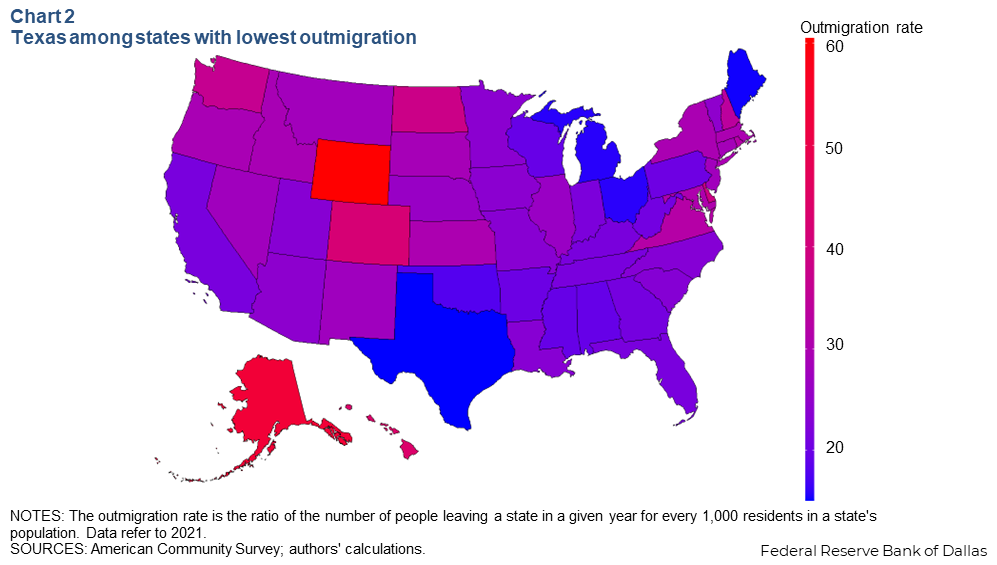 Downloadable chart | Chart data
Downloadable chart | Chart data
Overall outmigration numbers track everyone moving from one state to another state, including both people born there and those who moved there before leaving, making them a better indicator of population flows.
In addition to being the stickiest state, Texas had the lowest outmigration rate in 2021, followed by Maine and Michigan. Wyoming, Alaska and Hawaii experienced the highest outmigration rates.

Downloadable chart | Chart data